Tereza Pos (talk | contribs) (Created page with " Karyotypes and chromosomes can be distinquished by classical cytogenetic methods, such as <u>chromosome binding</u>. These methods visualize certain aspects and regions of c...") |
Tag: Source edit |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | Karyotypes and chromosomes can be distinquished by classical cytogenetic methods, such as <u>chromosome |
+ | Karyotypes and chromosomes can be distinquished by classical cytogenetic methods, such as <u>chromosome banding</u>. These methods visualize certain aspects and regions of chromosomes. Each chromosome has a unique banding pattern, therefore bands on chromosomes project the structure of the genome and its organisation. Each band usually contains from 5-10Mb. |
| + | |||
| + | Nearly all banding methods rely on harvesting chromosomes in mitosis. This is usually acchieved by treating cells with tubulin inhibitors (i.e. colchicine, colcemid) who depolymerize the mitotic spindle. |
||
==Methods of whole chromosome banding== |
==Methods of whole chromosome banding== |
||
===Q banding (Quinacridine Banding)=== |
===Q banding (Quinacridine Banding)=== |
||
| − | Was the first banding technique discovered (Caspersson et al., |
+ | Was the first banding technique discovered (Caspersson et al., 1969) and up to date it remains the simplest. Q banding uses fluorescent staining (i.e. by an DNA intercalating agent quinacridine) of metaphase chromosomes. Quinacrine banding is thought to reflect the distribution of rnoooooooooooooooo |
| − | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
===G banding (Giemsa Banding)=== |
===G banding (Giemsa Banding)=== |
||
Giemsa Banding is the most frequently used banding technique in cytogenetic laboratories. Chromosome G banding is usually performed either by the usage of trypsin (which removes chromosomal proteins) or by incubation in hot salt solutions (60°C) and then staining with Giemsa. Each chromosome pair stains in a distinctive pattern of light and dark bands. The dark bands are called G bands, and roughly correlate to base-pair composition (GC or AT) and repetitive DNA sequences. |
Giemsa Banding is the most frequently used banding technique in cytogenetic laboratories. Chromosome G banding is usually performed either by the usage of trypsin (which removes chromosomal proteins) or by incubation in hot salt solutions (60°C) and then staining with Giemsa. Each chromosome pair stains in a distinctive pattern of light and dark bands. The dark bands are called G bands, and roughly correlate to base-pair composition (GC or AT) and repetitive DNA sequences. |
||
| − | [[File:G-banding_chromosome_chart.gif|thumb|left| |
+ | [[File:G-banding_chromosome_chart.gif|thumb|left|452x452px|G-banding |
http://www.monctonhigh.ca/mcGBiology/cellular_division.htm]] |
http://www.monctonhigh.ca/mcGBiology/cellular_division.htm]] |
||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| Line 45: | Line 44: | ||
[[File:R_bands.jpg|thumb|left|400px|R-bands |
[[File:R_bands.jpg|thumb|left|400px|R-bands |
||
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/0471142905.hg0402s00/pdf]] |
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/0471142905.hg0402s00/pdf]] |
||
| + | |||
| Line 68: | Line 68: | ||
===Chromosome painting=== |
===Chromosome painting=== |
||
| + | Chromosome painting involves hybridization of each chromosome using a chromosome-specific with a unique combination of fluorescent dies. The provides a colorful array of chromosomes, each one painted a different color. |
||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Chromosome_painting.jpg|thumb|left|343px|Chromosome painting |
||
| + | http://carolguze.com/text/442-4-chromosome_analysis.shtml]] |
||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
==Methods of selective banding== |
==Methods of selective banding== |
||
| − | ===C banding=== |
+ | ===Centromere Heterochromatin Staining (C banding)=== |
| + | This technique, also known as CBG-staining and requires mild alkali treatment and Giemsa staining. It is used for banding of constitutive heterochromatin, therefore it is used i.e. for [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Centromere centromere] identification. It is also useful for staining of chromosomal regions, which contain repetitive DNA sequences (satellite DNA). These repetitive DNA sequences are ofthe located adjacent to centromeres and on the distal portion of the Y chromosome. The most significant bands are found on chromosomes 1,9,16 and Y. |
||
| − | Banding of constitutive heterochromatin. |
||
| + | [[File:C-banding.gif|thumb|left|360px|C banding |
||
| + | http://carolguze.com/text/442-4-chromosome_analysis.shtml]] |
||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
===T banding=== |
===T banding=== |
||
| − | Is a modification of R banding. |
+ | Is a modification of R banding. It is used for visualization of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Telomere telomeres] . |
| + | ===Nucleolar-Organizer-Region Staining (NOR STAINING)=== |
||
| − | ===Nor painting=== |
||
| + | This procedure requires a silver nitrate solution, consequently, it is sometimes reffered to as silver staining. It stains the active ribosomal [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nucleolus_organizer_region DNA-containing nucleolar organizer regions] in interphase nuclei. It is used for identification of human [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acrocentric#Acrocentric acrocentric] chromosomes 13, 14, 15, 21, and 22, for identification of marker chromosome origins and detection of trancription proteins in the NOR region. |
||
| + | [[File:Nor_banding.gif|thumb|left|400px|NOR banding |
||
| + | http://www.els.net/WileyCDA/ElsArticle/refId-a0005783.html]] |
||
| − | ===Cd-bands=== |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| − | ===D banding=== |
||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| ⚫ | |||
===Replication banding (BrdU)=== |
===Replication banding (BrdU)=== |
||
| − | Replication banding is based on the substitution of 5-bromo-2-deoxyuridine (BrdU) for thymidine during a defined portion of the S phase of the cell cycle. After substitution with BrdU, staining differentiates the DNA sequence with incorporated BrdU from the unsubstituted DNA. |
+ | Replication banding is based on the substitution of 5-bromo-2-deoxyuridine (BrdU) for thymidine during a defined portion of the S phase of the cell cycle. After substitution with BrdU, staining differentiates the DNA sequence with incorporated BrdU from the unsubstituted DNA. This technique is used for example for detection of reqions/sequences rich in AT pairs. |
| + | |||
| + | [[File:BrDu_banding.jpg|thumb|left|325px|BrdU banding |
||
| + | http://www.indmedica.com/journals.php?journalid=13&issueid=138&articleid=1827&action=article]] |
||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==References:== |
||
| + | Bickmore W.A., '''[http://web.udl.es/usuaris/e4650869/docencia/segoncicle/genclin98/recursos_classe_%28pdf%29/revisionsPDF/bandmethods2.pdf Karyotype Analysis and Chromosome Banding] , '''Encyclopedia of Life Sciences |
||
| + | |||
| + | '''[http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/0471142905.hg0402s00/pdf Chromosome banding techniques]''' , Current Protocols in Human genetics, '''1''' (2001) |
||
Latest revision as of 01:05, 17 March 2021
Karyotypes and chromosomes can be distinquished by classical cytogenetic methods, such as chromosome banding. These methods visualize certain aspects and regions of chromosomes. Each chromosome has a unique banding pattern, therefore bands on chromosomes project the structure of the genome and its organisation. Each band usually contains from 5-10Mb.
Nearly all banding methods rely on harvesting chromosomes in mitosis. This is usually acchieved by treating cells with tubulin inhibitors (i.e. colchicine, colcemid) who depolymerize the mitotic spindle.
Methods of whole chromosome banding[]
Q banding (Quinacridine Banding)[]
Was the first banding technique discovered (Caspersson et al., 1969) and up to date it remains the simplest. Q banding uses fluorescent staining (i.e. by an DNA intercalating agent quinacridine) of metaphase chromosomes. Quinacrine banding is thought to reflect the distribution of rnoooooooooooooooo
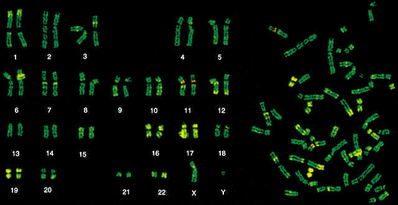
G banding (Giemsa Banding)[]
Giemsa Banding is the most frequently used banding technique in cytogenetic laboratories. Chromosome G banding is usually performed either by the usage of trypsin (which removes chromosomal proteins) or by incubation in hot salt solutions (60°C) and then staining with Giemsa. Each chromosome pair stains in a distinctive pattern of light and dark bands. The dark bands are called G bands, and roughly correlate to base-pair composition (GC or AT) and repetitive DNA sequences.

G-banding http://www.monctonhigh.ca/mcGBiology/cellular_division.htm
R banding (Reverse Banding)[]
Reversial towards the G and Q-banding patterns - i.e., a dark (positive) G-band is a light (negative) R-band and vice versa. R-banding can be used for chromosome identification, but G-banding is preferred. It is useful for visualization of telomeric ends. A basic protocol of R-banding inludes heating of slides at 88°C in a buffer, followed by Giemsa staining. R-bands represent euchromatin regions of chromosomes, which are GC rich.
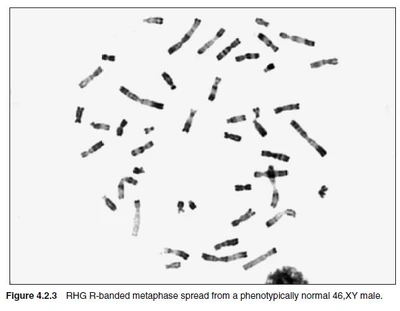
R-bands http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/0471142905.hg0402s00/pdf
Chromosome painting[]
Chromosome painting involves hybridization of each chromosome using a chromosome-specific with a unique combination of fluorescent dies. The provides a colorful array of chromosomes, each one painted a different color.
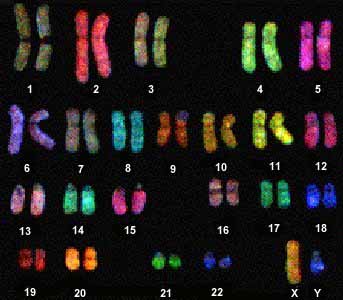
Chromosome painting http://carolguze.com/text/442-4-chromosome_analysis.shtml
Methods of selective banding[]
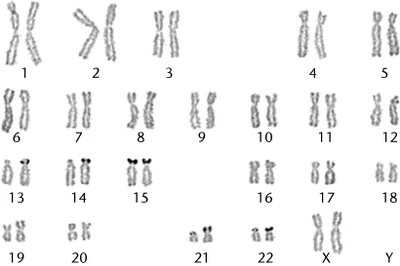
Centromere Heterochromatin Staining (C banding)[]
This technique, also known as CBG-staining and requires mild alkali treatment and Giemsa staining. It is used for banding of constitutive heterochromatin, therefore it is used i.e. for centromere identification. It is also useful for staining of chromosomal regions, which contain repetitive DNA sequences (satellite DNA). These repetitive DNA sequences are ofthe located adjacent to centromeres and on the distal portion of the Y chromosome. The most significant bands are found on chromosomes 1,9,16 and Y.

C banding http://carolguze.com/text/442-4-chromosome_analysis.shtml
T banding[]
Is a modification of R banding. It is used for visualization of telomeres .
Nucleolar-Organizer-Region Staining (NOR STAINING)[]
This procedure requires a silver nitrate solution, consequently, it is sometimes reffered to as silver staining. It stains the active ribosomal DNA-containing nucleolar organizer regions in interphase nuclei. It is used for identification of human acrocentric chromosomes 13, 14, 15, 21, and 22, for identification of marker chromosome origins and detection of trancription proteins in the NOR region.
NOR banding http://www.els.net/WileyCDA/ElsArticle/refId-a0005783.html
Methods of functional banding[]
Replication banding (BrdU)[]
Replication banding is based on the substitution of 5-bromo-2-deoxyuridine (BrdU) for thymidine during a defined portion of the S phase of the cell cycle. After substitution with BrdU, staining differentiates the DNA sequence with incorporated BrdU from the unsubstituted DNA. This technique is used for example for detection of reqions/sequences rich in AT pairs.

BrdU banding http://www.indmedica.com/journals.php?journalid=13&issueid=138&articleid=1827&action=article
References:[]
Bickmore W.A., Karyotype Analysis and Chromosome Banding , Encyclopedia of Life Sciences
Chromosome banding techniques , Current Protocols in Human genetics, 1 (2001)